Propulsion systems for Electric locomotives/ EMU/MEMU/Train Sets
The electric propulsion system used over Indian Railways employs AC or DC electric traction to drive locomotives. Powered by overhead catenary lines, typically delivering 25 kV AC at 50 Hz, electric power is transferred to the traction motors via pantographs and the propulsion system deployed for necessary conversion of power. Modern systems utilize three-phase induction motors or synchronous motors for efficient torque and speed control. Advanced propulsion systems include variable voltage, variable frequency (VVVF) drives for precise motor control, improving energy efficiency and reducing wear. Regenerative braking systems capture and reuse energy during braking by feeding it to the overhead supply network. The integration of power electronics enables smoother acceleration and deceleration, enhancing operational reliability and reducing maintenance. Indian Railways has progressively shifted from DC to AC systems for higher efficiency and power delivery on all routes. An important part of the propulsion system is the indigenously developed Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) in line with IEC 61375 standards which represents a significant stride towards technological self-reliance and operational efficiency in the rail sector.
Indian Railway at a Glance
th
Largest Railway Network in the World
KMs
Route length
KMs
Route deployed with KAVACH system
Stations with 18 Zones & 68 Divisions
Locos in commercial operation
EMUs in commercial operation
Passenger Vehicles
Coaching vehicles
Wagons
dedicated routes (Eastern and Western Corridor). for freight services
MT
of loading in last year
Tier-I city Equipped with Metro Service
Tier-II and Tier-III City being equipped with Metro service
%
Electrified
%
-
%
of CAGR (approx)
And More
Indian Market Overview
High Horsepower Freight E-Loco
E-Loco Propulsion
High-Speed Rail
Key Market Segments
Trainset
Metro
MRTS (EMU/MEMU)
Indian Market Overview
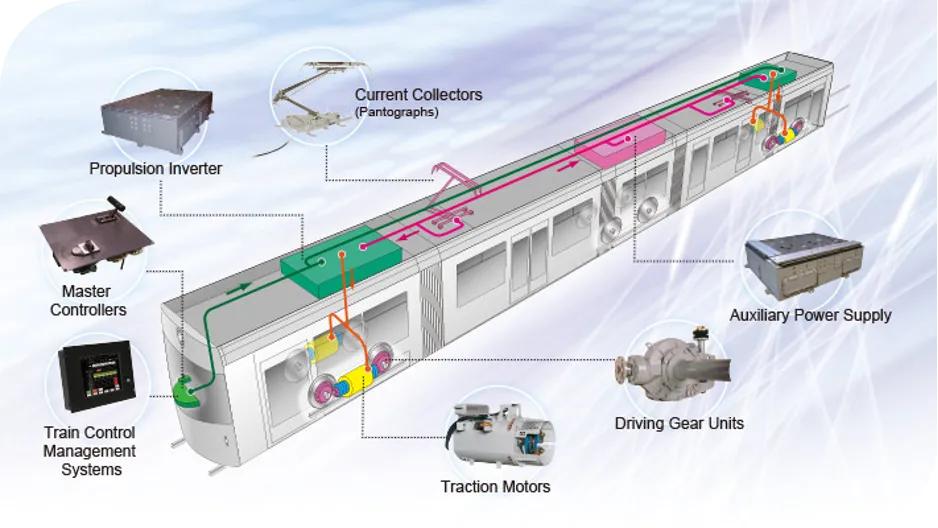
Key Components of Power Train of Rolling Stock
Vande Bharat at a Glance
The Vande Bharat trains utilize a sophisticated electric propulsion system powered by a 25 kV AC overhead catenary at 50 Hz. Electric power is transmitted via pantographs to the train’s traction motors. These motors are predominantly three-phase induction motor types, controlled by Variable Voltage, Variable Frequency (VVVF) drives for precise control/management of motor torque and speed.
The system features regenerative braking, which recovers energy during braking and returns it to the overhead supply, enhancing energy efficiency. Advanced power electronics ensure smooth acceleration and deceleration, with rates comparable to the Japanese high speed trains. The trains also include an indigenously developed Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) in compliance with IEC 61375 standards, reflecting significant progress in technological self-reliance and operational efficiency for Indian Railways.
Shortcomings
- Delay in Supply Compared to Urgency in Demand
- Only 3 out of Six Established Vendors are currently active.
- Dependency on outsourced vendors for most of the existing players.
- High rate of failures due to cost optimization leading to compromise on reliability.
- Inadequate after sales support by overseas Companies.
Winning Proposition
- Existing installed capacity is more than demand of Railways.
- Complete Product Ecosystem offering to end customer
-
Integrated Inhouse manufacturing :
- All electronics hardware and software
- All fabrication works for rolling stock
- Optimized overheads and assembly processes to lower price without compromising on reliability.
- Understanding of IR eco system and presence for after service support on PAN India basis.
